MacでElasticSearchをインストールしてMySQLのデータを日本語検索する
ElasticSearch本体のインストール
brew install elasticsearch
Plugin関連
Elasticsearch Head (クラスタ管理)
plugin -install mobz/elasticsearch-head
Marvel (クラスタモニタリングツール)
plugin -install elasticsearch/marvel/latest
http://localhost:9200/_plugin/marvel

Inquisitor Plugin (クエリのデバッグ)
plugin -install polyfractal/elasticsearch-inquisitor
http://localhost:9200/_plugin/inquisitor/#/

Kuromoji (日本語形態素解析エンジン)
plugin -install elasticsearch/elasticsearch-analysis-kuromoji/2.3.0
今回のメインの目的でもあるKuromojiのインストール
GitHubのページを見ると es-1.3系は Kuromoji2.3.0のようなので2.3.0をインストール
jdbc-connecterのインストール(この時の最新版5.1.33)
ダウンロードしてお好きな位置に配置
/Users/user_name/mysql-connector-java-5.1.33 に($HOME以下)配置
vi ~/.bashrc # 追記 export CLASSPATH=$CLASSPATH:/Users/user_name/mysql-connector-java-5.1.33/mysql-connector-java-5.1.33-bin.jar source ~/.bashrc
River (MySQLからデータを取り込み)
plugin --install jdbc --url http://xbib.org/repository/org/xbib/elasticsearch/plugin/elasticsearch-river-jdbc/1.3.4.4/elasticsearch-river-jdbc-1.3.4.4-plugin.zip
GitHubのReadmeにてmysql-connector-java-5.1.33-bin.jarをコピーする必要があるとの記載があるので、インストールディレクトリを確認する
>-> Installing jdbc... >Trying http://xbib.org/repository/org/xbib/elasticsearch/plugin/elasticsearch-river-jdbc/1.3.4.4/elasticsearch-river-jdbc-1.3.4.4-plugin.zip... >Downloading .........................................................DONE >Installed jdbc into /usr/local/var/lib/elasticsearch/plugins/jdbc
MySQL JDBC driver を $ES_HOME/plugins/jdbc/ にコピー
cp /Users/user_name/mysql-connector-java-5.1.33/mysql-connector-java-5.1.33-bin.jar /usr/local/var/lib/elasticsearch/plugins/jdbc
これでPlugin関連のインストールはOKなので
ElasticSearchの起動
$ elasticsearch
動作確認
Test indexの作成
curl -XPUT 'http://localhost:9200/test/'
戻り値
{"acknowledged":true}
defaultのanalyzerで検証
curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/test/_analyze?pretty=true' -d '東京都渋谷区'
戻り値
"tokens" : [ {
"token" : "東",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 1
}, {
"token" : "京",
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 2
}, {
"token" : "都",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 3
}, {
"token" : "渋",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 4
}, {
"token" : "谷",
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 5
}, {
"token" : "区",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 6,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 6
} ]
}
Kuromojiのanalyzerで検証
curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/test/_analyze?pretty=true&analyzer=kuromoji' -d '東京都渋谷区'
戻り値
$ curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/test/_analyze?pretty=true&analyzer=kuromoji' -d '東京都目黒区'
{
"tokens" : [ {
"token" : "東京",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 1
}, {
"token" : "都",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 2
}, {
"token" : "渋谷",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 3
}, {
"token" : "区",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 6,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 4
} ]
}
問題無く動作しているのでIndexの削除
curl -XDELETE 'http://localhost:9200/test'
戻り値
{"acknowledged":true}
最後にMySQLからデータの流し込み
ElasticSearch 側に kuromoji を使った検索インデックスを作成
curl -XPUT http://localhost:9200/test_kuromoji -d '{ "index": { "analysis": { "tokenizer": { "kuromoji_user_dict" : { "type":"kuromoji_tokenizer" } }, "analyzer": { "analyzer": { "type":"custom", "tokenizer": "kuromoji_user_dict" }}}}}'
Riverを使って、作成したインデックス(test_kuromoji)に MySQLデータベースサーバーからデータを取り込み
MySQLは
localhost
データベース名 = elasticsearchtest
test_table からデータを流し込む想定
curl -XPUT http://localhost:9200/_river/my_jdbc_river/_meta -d '{ "type": "jdbc", "jdbc": { "url": "jdbc:mysql://localhost/elasticsearchtest", "user": "root", "password": "password", "sql": "select * from test_table", "index": "test_kuromoji", "type": "test" }}'
最後にnameフィールドから"test"で検索してみる
curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/test_kuromoji/_search?pretty -d '{ "query": { "query_string": { "query": "name:テスト" } } }'
例えばidフィールドのみ取りたい場合
curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/test_kuromoji/_search?pretty -d '{ "query": { "match": { "name": "テスト"}}, fields: ["id"] }'
例えばさらにcreatedでソートして取りたい場合
curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/test_kuromoji/_search?pretty -d '{ "query": { "match": { "name": "テスト"}}, fields: ["id"], sort: [{created: {order: "desc"}}] }'
MySQLのFULLTEXTINDEXより、メチャクチャ速くなっていいのですがフロントのWebで検索エンジンとして使いたかったら、ページャー自作するしかないんですかね? 今時ページャー自作ってなーと。。。
参考サイト
http://dotnsf.blog.jp/archives/1005246681.html http://dotnsf.blog.jp/archives/1005213909.html http://tech.gmo-media.jp/post/70245090007/elasticsearch-kuromoji-japanese-fulltext-search http://qiita.com/yutori_enginner/items/bec071b2d9278f1b7e8f
各種ライブラリリンク先
http://www.elasticsearch.org/overview/elkdownloads/ http://xbib.org/repository/org/xbib/elasticsearch/plugin/elasticsearch-river-jdbc/ https://github.com/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-analysis-kuromoji
Rails + Grape と nginx + リバースプロキシでRESTfulなAPIサーバーを作ってみる
Rails + Grape と nginx + リバースプロキシでRESTfulなAPIサーバーを作ってみる
題名の通り、RESTfulなAPIサーバーを作りたくて最近の私の流れからRubyでやろうかなと。
ruby-toolboxのAPI_Buildersなどで見るとGrapeというのが一番人気なようでしたのでコレにしました。
この公式のGitHubにサンプルがたくさんあるのも良い点かと思います。
それで公式サイト以外にも検索して、Grapeのお作法みたいのをいろいろ調べたのですが、幾つかやり方とか書き方があるみたいでコレが正解とういうのはハッキリとは無さそうです。
ですので私のやり方以外にも多々書き方はあるかと思います。
更に、私はまだまだRuby on Rails + somethingは初心者の域を出ていないので、、、
以上よりGrapeを使用してAPIを作成しました。
またRailsを絶対に使う必要は無いと思いますが、結局多くの場合DBと連動するのでやはりmigrateが優れているRailsを使用しました。
(今は他のFWの学習コストを掛けたく無いなというもあります、、、)
なのでまずはいつも通りRailsの環境を用意します。
gem 'rails', '4.1.5' # For Grape API gem 'grape' gem 'grape-rabl' gem 'grape-jbuilder'
- その他多数。
- railsは4.1.5で動いているので一応記載。
ディレクトリ構成はこんな感じにしました。

通常のRailsの構成に、 api ディレクトリを足した形にしました。
検索するとcontrollersの中にapiディレクトリを切ってる方もいらっしゃいましたが特に制約は無いように思います。
今回は例として、Userに関する情報を扱うAPIとカテゴリ情報を扱うAPIを定義してみます。
以下編集していくファイルです
app/endpoint.rb
まずはGrape::APIを継承しているEndpoint::APIというクラスを作成します。
これでv1以下に設置されているAPIのmountを行い、定義されていないAPIのpathはすべて404で拾うようにしました。
require 'v1/user_api.rb'
require 'v1/category_api.rb'
module Endpoint
class API < Grape::API
mount UserApi::APIv1
mount CategoryApi::APIv1
route :any, '*path' do
error!({ error: 'Not Found',
detail: "No such route '#{request.path}'",
status: '404' },
404)
end
end
end
config/routes.rb
大本のroutesは先ほどのEndpoint::APIに "/api" でアクセスするよう向けてあげます
Rails.application.routes.draw do mount Endpoint::API => '/api' end
こんな感じになります。
$ rake routes
Prefix Verb URI Pattern Controller#Action
endpoint_api /api Endpoint::API
app/v1/user_api.rb
実際のuserに関する処理を行うAPIの実体ですね。 ファイル名はrailsの命名ルールに則って、 "_api" を付けてます。
module UserApi
class APIv1 < Grape::API
format :json
default_format :json
version "v1", using: :path
helpers do
# Model User のStrong parameterをここで定義
def user_params
ActionController::Parameters.new(params).permit(:id, :name, :device_id, :status, :signed_out)
end
end
resource :user do # ここで定義したresourceがURLになります。(=/api/v1/user)
desc "Return each user data"
# GET /api/v1/user/:id
get ':id' do
User.find(params[:id])
end
desc "Return all user datas"
# GET /api/v1/user
get do
User.all
end
desc "Update a status"
params do
requires :id, type: String, desc: "Status ID."
requires :status, type: String, desc: "Your status."
end
put ':id' do
current_user.statuses.find(params[:id]).update({
status: params[:status]
})
end
desc "Delete a status"
# Don't allow to delte user from api
desc "Entry new user"
# POST /api/v1/user
# For example, the request should be like this
# curl -d '{
# "id": "39784",
# "name": "test_user_39784",
# "device_id": "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx",
# "status": "",
# "sigined_out": false
# }' -X POST -H "Content-Type:application/json, Accept-Version:v1" https://localhost:3000/api/v1/user
params do
requires :id, type: String
requires :name, type: String
requires :device_id, type: String, regexp: /^[0-9A-Za-z_-]+$/
optional :status, type: String, desc: "Your status."
optional :signed_out, type: Boolean, default: false
end
post do
@user = User.new(user_params);
@user.save!
# Return created
status 201
end
end
end
end
REST設計
| 機能 | method + URL |
|---|---|
| ユーザ一覧を取得 | GET /api/v1/user |
| 1ユーザを取得 | GET /api/v1/user/1 |
| 新しいユーザを追加 | POST /api/v1/user |
| 既存のユーザを修正 | PUT /api/v1/user/1 |
| 既存のユーザを削除 | DELETE /api/v1/user/1 |
このRESTの思想に沿って、それぞれ定義してあります。
例では、APIからのユーザ削除は受け付けない(定義してない)など。
登録する時の "# POST /api/v1/user" などが一番需要があるかと思いますが、 "params do" 内を見て頂くと この例では、POSTで引数にjson形式のデータを受け取る定義になっています。
user_api.rb上部にて
default_format :json version "v1", using: :path
jsonの中身は、id, name, device_idは必須としていて、statusとsigned_outは無くても良くしてあります。
またdevice_idは正規表現で形式を絞ってあります。
このような形でsave!で例外が発生しなければ、response:status_codeを201で返します。
さらに、 "helpers do" 自由にhlper関数を定義できるのでここではUserテーブルのStrong Parameterを定義してあります。
それで後はAPIをV2にバージョンアップしたければ、それぞれクラス毎にアップデータできます。
概要が飲み込めれば比較的簡単に短時間でAPIが作成できるので、とても便利なモジュールだと思います。
ただこのままですとURLにバージョンが入っていてイケてないので、次のエントリーでnginxの設定でアクセス元が何も変更すること無く バージョンを切り替えられるよう対応したいと思います。
nginx / ruby / unicorn を作りたいDockerfile
centosに、ベースとなる環境作成したければこんなイメージになるかと
FROM centos # Install initail modules RUN yum update -y RUN yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ make openssl-devel build-essential curl openssl openssl-devel readline-devel readline compat-readline5 git zlib1g-dev libssl-dev libreadline-dev libyaml-dev ruby-devel svn autoconf bison RUN yum -y --enablerepo=epel,remi,rpmforge install libxml2 libxml2-devel RUN yum -y --enablerepo=epel,remi,rpmforge install libxslt libxslt-devel RUN yum -y install sqlite-devel RUN yum -y install vim RUN yum -y install sudo RUN yum -y install passwd RUN yum -y install tar RUN yum -y install python-setuptools # Install SSH RUN yum -y install openssh RUN yum -y install openssh-server RUN yum -y install openssh-clients RUN yum -y install mysql-client mysql-devel mysql-shared #RUN passwd -f -u ec2-user #ADD ./authorized_keys /home/ec2-user/.ssh/authorized_keys # Create User RUN useradd docker #RUN echo 'docker:dockerpasswd' | chpasswd RUN yes docker | passwd docker # Set up SSH #RUN mkdir -p /home/docker/.ssh #RUN chown docker /home/docker/.ssh #RUN chmod 700 /home/docker/.ssh #ADD authorized_keys /home/docker/.ssh/authorized_keys #RUN chown docker /home/docker/.ssh/authorized_keys #RUN chmod 600 /home/docker/.ssh/authorized_keys RUN sed -ri 's/UsePAM yes/#UsePAM yes/g' /etc/ssh/sshd_config RUN sed -ri 's/#UsePAM no/UsePAM no/g' /etc/ssh/sshd_config #RUN service sshd start #RUN service sshd stop # Insatall rbenv, ruby-build RUN git clone https://github.com/sstephenson/rbenv.git /root/.rbenv RUN mkdir -p ~/.rbenv/plugins ENV PATH /root/.rbenv/bin:$PATH RUN echo 'eval "$(rbenv init -)"' >> /etc/profile.d/rbenv.sh RUN echo 'eval "$(rbenv init -)"' >> .bashrc RUN bash -lc 'source .bashrc' RUN git clone https://github.com/sstephenson/ruby-build.git ~/.rbenv/plugins/ruby-build # Install Ruby ENV CONFIGURE_OPTS --disable-install-doc RUN echo 'gem: --no-rdoc --no-ri' >> /.gemrc RUN bash -lc 'rbenv install 2.1.2' RUN bash -lc 'rbenv rehash' RUN bash -lc 'rbenv global 2.1.2' RUN bash -l -c 'ruby -v' RUN bash -lc 'gem install bundler' # clone application form github RUN mkdir -p /var/www RUN git clone https://github.com/YOUR_REPOSITORY/YOUR_PROJECT.git /var/www/rails WORKDIR /var/www/rails # Set up rails RUN bash -l -c 'bundle config build.nokogiri --use-system-libraries' RUN gem install nokogiri -v '1.6.2.1' -- --use-system-libraries --no-rdoc --no-ri RUN gem install mysql2 -v '0.3.16' --no-rdoc --no-ri #RUN bash -l -c 'bundle install' #RUN bash -l -c 'bundle exec rake db:create RAILS_ENV=production; bundle exec rake db:migrate RAILS_ENV=production' #RUN bash -l -c 'bundle exec rake master:import' #ADD ./secrets.yml /var/www/rails/config/secrets.yml # nginx RUN rpm -ivh http://nginx.org/packages/centos/6/noarch/RPMS/nginx-release-centos-6-0.el6.ngx.noarch.rpm RUN yum -y install nginx # Install MySQL Client RUN yum -y --enablerepo=remi,epel,rpmforge install mysql-client mysql-devel # Install supervisord RUN easy_install supervisor # supervisord RUN echo_supervisord_conf > /etc/supervisord.conf RUN echo '[include]' >> /etc/supervisord.conf RUN echo 'files = supervisord/conf/*.conf' >> /etc/supervisord.conf RUN mkdir -p /etc/supervisord/conf/ ADD supervisor.conf /etc/supervisord/conf/service.conf EXPOSE 22 80 3000 CMD bash -l -c 'bundle exec rails s' # Run supervisord at startup CMD ["/usr/bin/supervisord"]
GitHub Pagesがとても便利な件
スタティックなページを楽にサクサクと作るというような事があまり最近は無かったので知らなかったのですが GitHub Pagesがとても便利だったのでメモを残しておきます。
xxx.github.ioとかでも作成したページは見れるのですが、普通は独自のドメインでやりたいはずです。
通常自分で独自ドメインのGitHub Pagesを作りたい場合は
を準備して、リポジトリ名:<アカウント名>.github.io で作ったものに対してCNAMEという名前のファイルを作成して向ければいいようです。
具体的にはリポジトリ内にCNAMEを作成して、向けたいドメインを記載しリポジトリにプッシュします。
$ dig あなたの独自ドメイン ; <<>> DiG 9.8.3-P1 <<>>あなたの独自ドメイン ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 18669 ;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 3, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 0 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;あなたの独自ドメイン. IN A ;; ANSWER SECTION: あなたの独自ドメイン. 300 IN CNAME <あなたのアカウント名>.github.io. <あなたのアカウント名>.github.io. 1349 IN CNAME github.map.fastly.net. github.map.fastly.net. 20 IN A 103.245.222.133
のように向けたいドメインが <あなたのアカウント名>.github.ioのCNAME になっていれば成功です。
とっても簡単で便利ですね〜
Circle Ciでlocalhostへ設定してあるfluentdを使用する方法とcircle.yml
現在とあるRuby on RailsのプロジェクトでCircle Ciを使っているのですが、その中でfluent-logger-rubyを使っています。
Fluent::Logger::FluentLogger.open(nil, :host => localhost, :port => 24224)
こんな感じですね。 それでこれをまんまCircle CiでRspecしようとすると、当然Circle Ciのログで
ERROR -- : Failed to connect fluentd: Connection refused - connect(2) for "localhost" port 24224
とエラーが出てfailしてしまいます。
どうしたものかわからなかったので、Live Supportに問い合わせたところ「sudo出来るように設定を変更するので、そこでapt getでもして」という回答をもらったので、それを反映したcircle.ymlがこちら
machine:
ruby:
version: 2.1.2
dependencies:
pre:
- curl -L http://toolbelt.treasure-data.com/sh/install-ubuntu-precise.sh | sh
- sudo cp config/circle/td-agent.conf /etc/td-agent/td-agent.conf
- sudo /etc/init.d/td-agent stop
- sudo /etc/init.d/td-agent start
database:
override:
- mv config/circle/database.yml config/database.yml
- bundle exec rake db:create db:migrate db:seed --trace
Circle Ci用の設定ファイルが複数になったので、config/circle/ 以下に入れています。
config/circle/td-agent.confの中身は単純にこんな感じです
<source>
type forward
port 24224
bind 0.0.0.0
</source>
<match **>
type stdout
</match>
これでRspecがfluentdアクセスの部分でエラーを吐く事は無くなりました。
でもCircleCi + fluentd 使ってる方たちって他どうやってるんでしょうかね?検索してもあまり事例なかったので。
あとついでにもう一つ気になっているのが、EC2上のサーバにDeployする時のSSHのSecurityGroupの設定なんですが これも皆さんどうしてるものなんですかね?
今回は別途chefでサーバを作っていますが、capistranoからaws-sdkを用いてもDockerだとしても、CircleCiからEC2サーバに何かさせる時に どうするか?という点では同じかと。
CircleのSourceで全部やってるんですかね???
なので該当のサーバからtemporaryで空けてやっています。
そのスクリプトはこのクラスメソッドさんのエントリ のが良いので
参考にさせて頂いて、このDeploy用のIAM circleciを用意して都度Open/Closeしています。
具体的には
config/circle/openssh.sh
#!/bin/sh
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID>
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=<AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY>
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=ap-northeast-1
MYSECURITYGROUP=<MYSECURITYGROUP>
MYIP=`curl -s ifconfig.me`
aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress --group-id $MYSECURITYGROUP --protocol tcp --port 22 --cidr $MYIP/32
config/circle/closessh.sh
#!/bin/sh
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID>
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=<AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY>
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=ap-northeast-1
MYSECURITYGROUP=<MYSECURITYGROUP>
MYIP=`curl -s ifconfig.me`
aws ec2 revoke-security-group-ingress --group-id $MYSECURITYGROUP --protocol tcp --port 22 --cidr $MYIP/32
ただし、現状のCircleCiのUbuntuに入っているawsコマンドはバージョンが古いのでこれをそのまま事項すると
--group-id: mispelled meta parameter?
とエラーになってしまうので、バージョンUPするコマンドもcircle.ymlに忍ばせています。
machine:
ruby:
version: 2.1.2
hosts:
localhost: 127.0.0.1
staging-web: xx.xx.xx.xx
dependencies:
pre:
- curl -L http://toolbelt.treasure-data.com/sh/install-ubuntu-precise.sh | sh
- sudo cp config/circle/td-agent.conf /etc/td-agent/td-agent.conf
- sudo /etc/init.d/td-agent stop
- sudo /etc/init.d/td-agent start
- sudo pip install awscli
database:
override:
- mv config/circle/database.yml config/database.yml
- bundle exec rake db:create db:migrate db:seed --trace
deployment:
staging:
branch: master
commands:
- sh config/circle/openssh.sh
- bundle exec cap staging deploy
- sh config/circle/closessh.sh
といった感じなのですが。
欠点は全体的に時間がかかってしまう事ですかね〜
Error:Execution failed for task ':app:processDebugManifest'.
Android Studioにて下記エラーが発生した祭の対応方法
Error:Execution failed for task ':app:processDebugManifest'.
Manifest merger failed with multiple errors, see logs
Android Studioのバージョンは現時点で最新の0.8.2

追加インストールしたAndroid SDKは
* Android SDK Tools
* Android SDK Platform-tools
* Android SDK Build-tools
* Android L
* Android 4.4W
* Android 4.4.2
* Android Support Repository
* Android Support Library
です。
それで上記のようなエラーが出るので、logを見てみると
uses-sdk:minSdkVersion 8 cannot be smaller than version L declared in library com.android.support:support-v4:21.0.0-rc1
というログが出ていました。 調べていると * uses-sdkを削除する * Manifest.xmlのmanifestタグに xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" を追記する
など幾つか出てきましたが、結局は
compile 'com.android.support:support-v4:+'
が悪さをしていました。
app/build.gradleのdependenciesセクションの記載を以下の追加or変更するか、
dependencies {
# ここに他にもcompile files記載があるかもしれません
compile 'com.android.support:support-v4:20.0.0'
}
あるいは、Android Studioのmenu->File->Project Structure->Dependenciesタブから
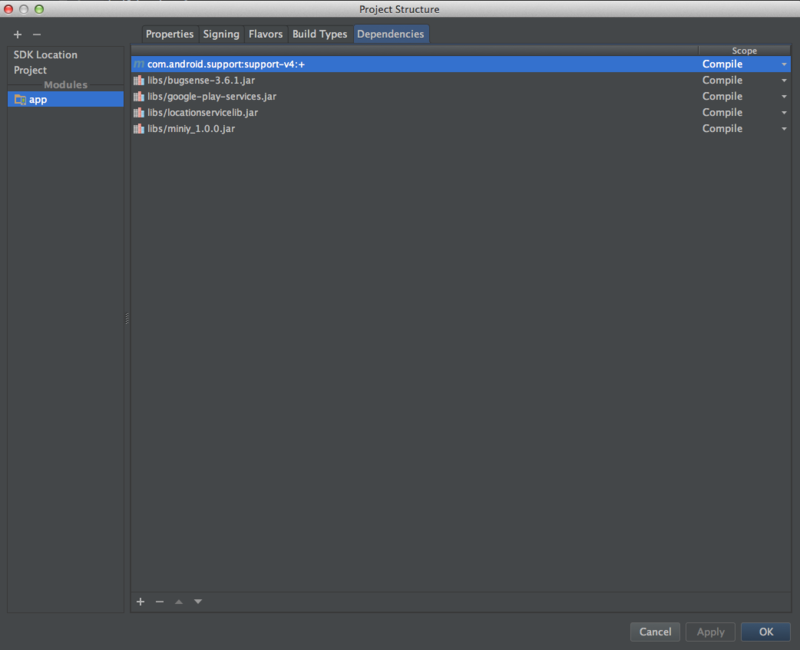
のcompile 'com.android.support:support-v4:+'を削除し、代わりに
compile 'com.android.support:support-v4:20.0.0'
を追加することで解決出来ました。
EC2にruby + nginx+passengerをインストールする
Macからchefを用いてEC2にruby + nginx + passengerをインストールする方法
先日 nginx+unicorn の記事を書いたばかりなのですが、ActionController::Liveを使いたい状況になって ActionController::LiveはPassengerかPumaじゃないと動かないと知ったためPassenger環境を作る事にしました。
Passenver vs Pumaはこちらの記事を参考にPassengerにしようと。
参考
インストール後の全体的なバージョン
$ rbenv -v
rbenv 0.4.0-98-g13a474c$ ruby -v
ruby 2.1.2p95 (2014-05-08 revision 45877) [x86_64-linux]$ /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -v
nginx version: nginx/1.4.7$ passenger -v
Phusion Passenger version 4.0.48
"Phusion Passenger" is a trademark of Hongli Lai & Ninh Bui.
ハマったのは2つ
コンパイルが通らない
passenger-install-nginx-moduleが動き出して、だいぶ待ったあとにvirtual memory exhausted: Cannot allocate memory
rake aborted!
と出たのですが、これはもう言葉の通りでEC2のt2.microではメモリが足りなくてコンパイル出来ませんでした。
t2.small以上を選択する必要があります。
nginxが起動出来ない
nginx startするとnginx: [alert] Unable to start the Phusion Passenger watchdog because its executable (/usr/local/rbenv/versions/2.1.2/lib/ruby/gems/2.1.0/gems/passenger-4.0.48/buildout/agents/PassengerWatchdog) does not exist. This probably means that your Phusion Passenger installation
というエラーが出てしまう点で、それは結局はnginx.confのレシピのpassenger_rootの設定が間違っているためでした。
検索すると、SELinuxをdisableしろみたいなStackOverFlowがあるのですが結局は関係ありませんでした。(私は何も変更してないです)
その対応方法ですが、公式ドキュメントのここを読むと
2.3.3. Inserting passenger_root into nginx.conf
$ passenger-config --root
コマンドでnginx.confに設定すべきpassenger_rootがわかるのでご自身の環境に合わせてください。
$ passenger-config --root
/usr/local/share/ruby/gems/2.0/gems/passenger-4.0.48
passenger4nginxのレシピを変更しなければこうなるはずです。
このまま$ git cloneされるなら、コマンドは簡単です。
まずはいつも通り、knifeコマンドがssh出来るよう .ssh/config に設定を記載
$ vi ~/.ssh/config
Host server
Hostname 0.0.0.0
User ec2-user
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/server.pem`
sshが通ることを確認して
$ knife solo prepare server
$ knife solo cook server
今回の全レシピはここにあります
rbenvとnginxのコンパイルに超時間がかかるので、お昼休み前に実行される事をオススメします。
P.S
あとこの記事からMarkdown記法に変えましたw